top of page
Hani Sbitany, MD
Chief of Plastic & Reconstructive surgery
Specialist in Breast REconstruction Surgery
Mt Sinai West Medical Center
New York City
Implant based breast reconstruction
Bilateral Mastectomies and Prepectoral Implant Reconstruction

Preoperative

Postoperative
Left Mastectomy and Prepectoral Implant Reconstruction

Preoperative

Postoperative
Delayed Right Breast Prepectoral Implant Reconstruction

Preoperative

Postoperative
Bilateral Mastectomies and Prepectoral Implant Reconstruction

Preoperative
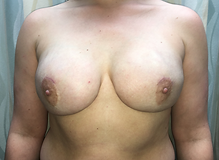
Postoperative
The most common method of breast reconstruction surgery in the United States uses tissue expanders and breast implants. This can be performed as either a two-staged procedure, or a single-stage procedure, based on what is safest for the patient.
With two-stage operations, the first stage involves placement of the tissue expander. This can either be done at the time of the mastectomy (for immediate reconstruction patients) or after the mastectomy has healed (for delayed reconstruction patients). The tissue expander is an implant that goes in empty, and can be filled after surgery in the office, over a few visits. This allows gentle, safe re-stretching of the breast skin. The expander is filled with saline, until a volume is reached that allows for placement of a breast implant of the desired size.
Once this stretching (expansion) is complete, the second-stage surgery is planned. The second surgery involves removal of the filled tissue expander, and placement of a permanent breast implant in its place.
Some patients may be candidates for direct-to-implant reconstruction whereby the permanent implant is inserted immediately without going through the tissue expander and expansion process. With this approach, the permanent implant is placed at the time of mastectomy. The decision to proceed with direct-to-implant reconstruction is made on a number of criteria, including safety, patient's desired breast size, and anticipated treatments needed for breast cancer treatment.
Dr. Sbitany will help you navigate these options, and select the one that is safest and best for you.
bottom of page